Introduction
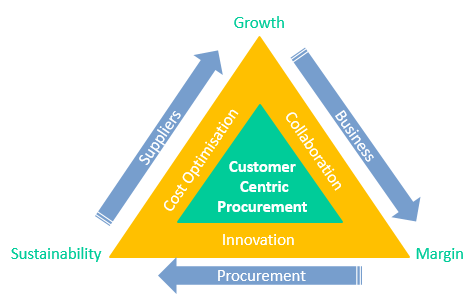
Increasingly, organizations see Supply Management as a core ‘must get right’ competency. In leading organizations around the world supply management is beginning to take an active role in product innovation and brand management, which require the critical skills incorporated into procurement’s golden triangle.
These organizations realize that a large part of their relationship with end customers is in fact, dependent upon their suppliers and that Supply Management is no longer just about consolidating the supplier base, establishing long-term contracts and leveraging spend potential. In these organizations procurement’s strategic impact it is increasingly measured by its effectiveness in new product development, collaboration, innovation, and enhancing customer satisfaction. This customer-centric procurement is at the heart of ‘Procurement’s Golden Triangle’:
Cost Optimization
Value-based procurement strategies can have a significant impact on company performance by capturing and harnessing value from suppliers. M&A highlights this contribution where up to 70% of the benefit of M&A can come from procurement activities.
Procurement Excellence can enable organization’s to drive both ‘cost down’ and ‘cost out’ of the supply chain while simultaneously delivering additional ‘value.’
The need to switch from ‘cost’ to ‘value, is increasingly recognized by procurement leaders, who retain control of all processes essential to meeting their corporate strategies and outsource less strategic activities to their chosen partners.
By developing market scanning capabilities to understand how markets are changing and how their processes must adapt to meet these changes procurement can identify the core processes needed to support company strategies and determine those done in-house and which should be outsourced.
Strategic cost management capability is not an accident. It is not a knee-jerk response to a down cycle. Excellence occurs as a result of sound business processes and applied ability whatever the economic cycle. It is embedded into the organization through a formal governance and control structure that inserts cost optimization into the very culture of the organization.
Achieve the three goals of strategic procurement in the business value chain provides the systematic approach most likely to provide sustainable cost leadership.
For Supply Management the strategic goals must be:
- Building Capability in Supply Management
- Become a Source for Cost Leadership
- Become a Source for Product and Service Differentiation
Such goals require Supply Management to understand the nature and significance of costs for business performance, considering cost in the context of the benefits they produce. The critical question for procurement in this context becomes not.
‘how much does it cost?’,
but
‘what are the benefits it will produce?’
and
‘how can the business best organize to manage cost to gain a competitive advantage?’
Collaboration
Mastering collaboration is a key to sustaining competitive advantage. Innovations are now increasingly brought to market by collaborators external to the organization in a seeker – solver model, coordinated by the seeker organization. CPO’s must now develop collaborative strategies that include:
- Recognizing collaboration as a strategic capability
- Organizing effectively for collaboration
- Investing over the long term to establish collaborative skills.
Collaboration can be used to create value that competitors cannot easily replicate. It aims specifically at creating a gap between the organization and its direct competitors to develop a sustainable competitive advantage, improved margins, and sustainable growth, by exploiting capabilities to their advantage rather than for the benefit of the industry as a whole.
Procurement can contribute to securing a competitive advantage by focusing on their organization’s generic strategies around overall cost leadership, differentiation, or a combination of the two.
CPO’s should seek to achieve best practice status on multiple dimensions of excellence:
- Product/Service: Design, experience, look, touch, feel, etc. – e.g., Apple
- Differentiation: Product, Service, Brand, eg., Starbucks
- Marketing Advantages: Distribution cost, the route to market – eg., Amazon
- Cost Advantages: Cost of goods and services, administration expenses, e.g., Dell, Wall Mart
- Financial Advantages: Mergers and acquisitions, cash flow
Procurement strategies can add value to create a competitive advantage in each dimension if they are; valuable, rare, costly to imitate, not substitutable.
Innovation
Leading on innovation places the skills and responsibilities of the procurement function right at the heart of its process. Helping define needs, identifying and evaluating potential suppliers, negotiating complex deals and managing long-term partnerships with suppliers are activities that procurement understands and has a track record of delivery.
The challenge for procurement is to develop the new skills required when dealing with intellectual property; they must:
- Engage supply markets without revealing critical details about their intentions
- Have the tools to evaluate how much they are willing to pay to explore and develop new ideas
- Collaborate and to build partnerships that build preferential relationships with suppliers
The opportunity for CPO’s to support their company’s innovation program is a significant one. By creating alignment across the organization and integrating procurement both internally and with suppliers and customers alike the CPO can:
- Gain equal status for procurement with other functions
- Install a real belief in suppliers as valuable allies and not merely cost levers
- Deliver quick benefits to internal customers, to prove the value of procurement in innovation
Procurement has existing core competencies that support innovation which in turn supports growth.
Procurement’s Golden Triangle Conclusion
Supply management has captured the stage and must now set the scene to foster closer integration with their organization’s customer-facing functions to get closer to the customer. The aim is to achieve:
- Greater emphasis on internal and external collaboration between partners
- Increased focus on value, creation, and delivery
- More stringent definition of customer satisfaction
- Faster decision-making cycles
By understanding the supply chain from the customers perspective and building a network of suppliers who not only have the desired capabilities but are also committed to both your organizations and your customer’s goals and objectives, Supply Management can direct strategy and operations to drive sustainable growth from a position of competitive advantage.
Nuff said …